What is an HIV RNA test and how is it used for diagnosis? This test detects the presence of the virus in the blood by identifying its genetic material. It’s often used in early stages of infection when antibodies may not yet be detectable. Is it a reliable method for HIV diagnosis?
HIV RNA testing is a type of diagnostic test that detects the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in the bloodstream. Unlike traditional HIV antibody testing, which detects antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the virus, RNA testing looks for the genetic material of the virus itself. This allows for much earlier detection of HIV, as the RNA test can detect the virus as early as 9-11 days after infection, compared to the 2-4 week window period for antibody testing.
If you are at risk for HIV infection, getting an HIV RNA test can provide you with peace of mind and help you take control of your health. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about HIV RNA testing, including how it works, when to get tested, and what to expect during and after the test.
How Does HIV RNA Testing Work?
HIV RNA testing works by detecting the genetic material of the virus in the bloodstream. During an HIV infection, the virus replicates rapidly, producing copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. RNA testing looks for a specific type of RNA called the “viral load,” which measures the amount of virus in the bloodstream.
To perform an HIV RNA test, a healthcare provider will take a small blood sample from your arm. The sample will then be sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory will use a technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to amplify any viral RNA that may be present in the sample. If the viral load is above a certain threshold, the test will be considered positive.
When Should You Get an HIV RNA Test?
HIV RNA testing is most commonly used for early detection of HIV in people who are at high risk for infection. This includes individuals who have recently engaged in high-risk sexual behavior or shared needles with someone who may have HIV. It is also recommended for people who may have been exposed to HIV in a healthcare setting, such as through a needlestick injury.
In addition to early detection, HIV RNA testing can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of HIV treatment. If you are living with HIV, your healthcare provider may use RNA testing to measure your viral load and determine whether your treatment is working effectively.
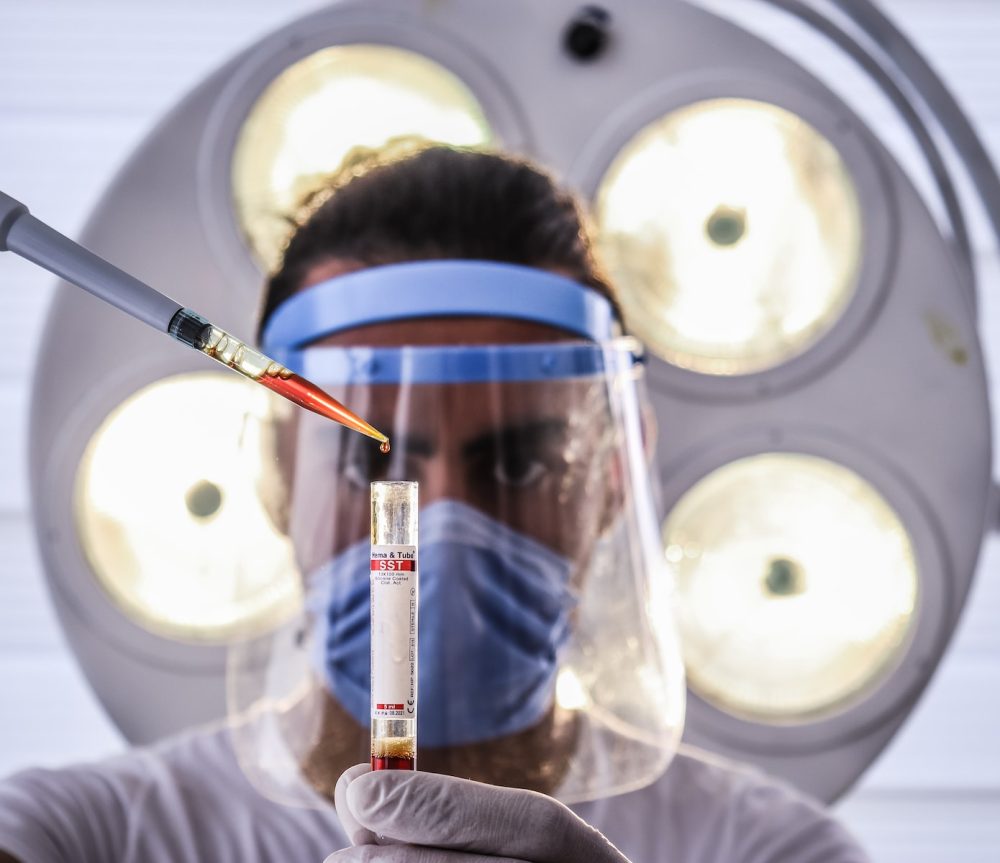
What to Expect During an HIV RNA Test
Getting an HIV RNA test is a simple and straightforward process. Before the test, your healthcare provider will explain the procedure and answer any questions you may have. You will then be asked to provide a blood sample, which will be taken from your arm using a needle.
Some people may experience mild discomfort or a slight pinch when the needle is inserted. However, the procedure is generally painless and takes only a few minutes to complete.
After the test, your healthcare provider will explain the results and what they mean for your health. If the test is positive, it does not necessarily mean that you have HIV. False positives can occur, especially if the viral load is low. Your healthcare provider may recommend follow-up testing to confirm the results.
If the test is negative, it means that no viral RNA was detected in your bloodstream. However, it is important to remember that HIV RNA testing only detects the virus during the acute phase of infection. If you have engaged in high-risk behavior, you may need to get tested again at a later time to ensure that you are not infected.